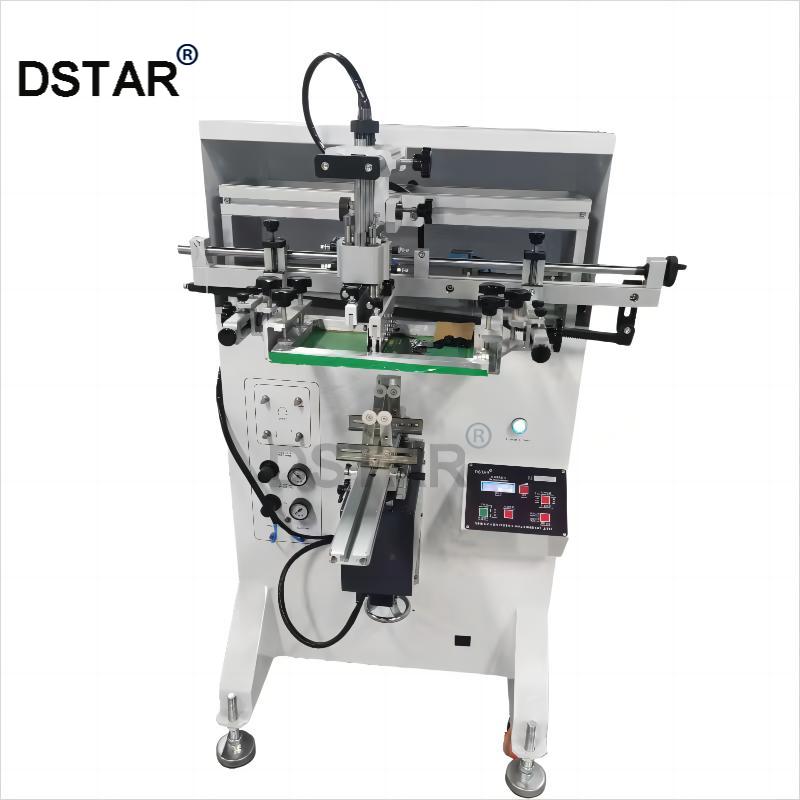
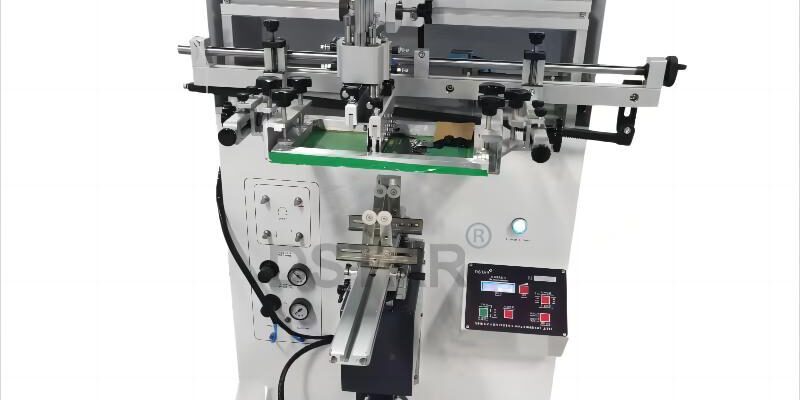
Product: bottle serigraphy printing machine
Model:DX-400
Printing color:1 color
Max screen plate size:L400*W550mm
Min screen plate size:L200*W300mm
Work table size:350*220mm
Max printing length:380mm
Max printing diameter:φ110mm
Arc:280mm
Taper angle:±7-15°
Max printing speed:1100 pcs/hr
Vertical stroke:100mm
Horizontal stroke:400mm
Vertical adjustable:100mm
Machine size:L89*W86*H130cm
N.W:130KGS
Screen printing consumables
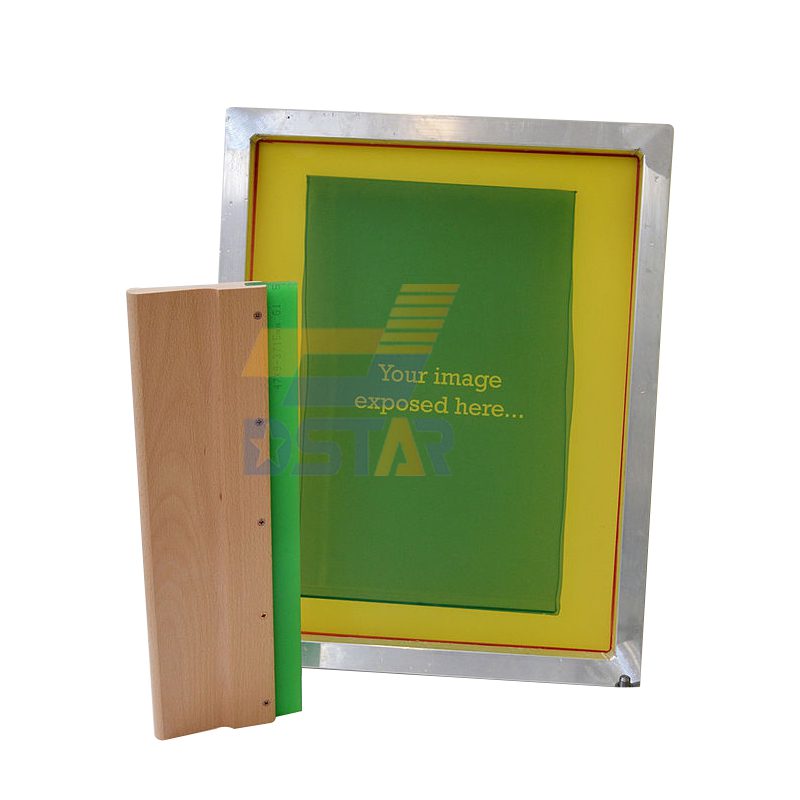



What is screen printing?
Screen printing, also known as silk screening, is a printing technique that involves using a mesh screen to transfer ink onto a substrate, such as paper, fabric, metal, plastic, or glass. It’s a versatile method suitable for printing on a wide range of surfaces and materials, making it popular in various industries including textiles, signage, packaging, electronics, and more.
Here’s an overview of the screen printing process:
- Preparation of the Screen: A mesh screen, typically made of polyester or nylon, is stretched tightly over a frame (usually made of aluminum or wood) to create a flat, taut surface. The screen is then coated with a light-sensitive emulsion.
- Image Preparation: A stencil, also known as a screen printing film or screen printing positive, is created by blocking out areas of the screen using a light-blocking material, leaving open the areas through which ink will pass onto the substrate. This can be done manually or digitally using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Exposure: The prepared screen is then exposed to a light source, usually UV light, with the stencil in place. The light causes the emulsion to harden and bond to the mesh in the open areas of the stencil, while the covered areas remain soft and water-soluble.
- Washing: After exposure, the screen is washed with water, which removes the soft emulsion, leaving behind a negative image of the stencil on the screen. This negative image corresponds to the areas where ink will be transferred onto the substrate.
- Printing: The screen is placed onto the substrate, and ink is applied to the top of the screen. A squeegee is then used to spread the ink evenly across the screen, forcing it through the mesh and onto the substrate in the open areas of the stencil.
- Curing: Once the ink is applied, the substrate is passed through a drying or curing process, which may involve heat curing, air drying, or UV curing, depending on the type of ink used and the substrate material. This ensures that the ink bonds securely to the substrate and achieves the desired durability and colorfastness.
- Repeat: The process is repeated for each color in the design, with additional screens and stencils created as needed for multicolor prints.
Screen printing offers several advantages, including:
- Versatility in printing on various substrates and materials.
- Ability to produce vibrant colors and opaque prints.
- Long-lasting and durable prints, suitable for outdoor use and industrial applications.
- Cost-effectiveness for large production runs.
However, screen printing also has limitations, such as the complexity and setup time required for creating screens and stencils, as well as the difficulty in achieving fine detail compared to digital printing methods. Overall, screen printing remains a popular choice for many applications due to its versatility, durability, and ability to produce high-quality prints.
Screen printing application:
Screen printing is a versatile printing method that can be applied to a wide range of products across various industries. Some common products that are often screen printed include:


- Apparel and textiles
- Promotional products
- Signage and banners
- Packaging
- Electronics
- Glassware and ceramics
- Automotive and industrial products
- Fine art and posters
- Sporting goods
- Home furnishings and décor
These are just a few examples of the many products that can be screen printed. The versatility, durability, and cost-effectiveness of screen printing make it a popular choice for a wide range of applications in various industries.







